Presentation
Learning and Innovating are two fundamental needs of modern societies. The purpose of our research is to produce knowledge on learning and innovation ecosystems for a responsible and sustainable experience and development of individuals, organizations and territories.
In this page :
Learning and Innovating
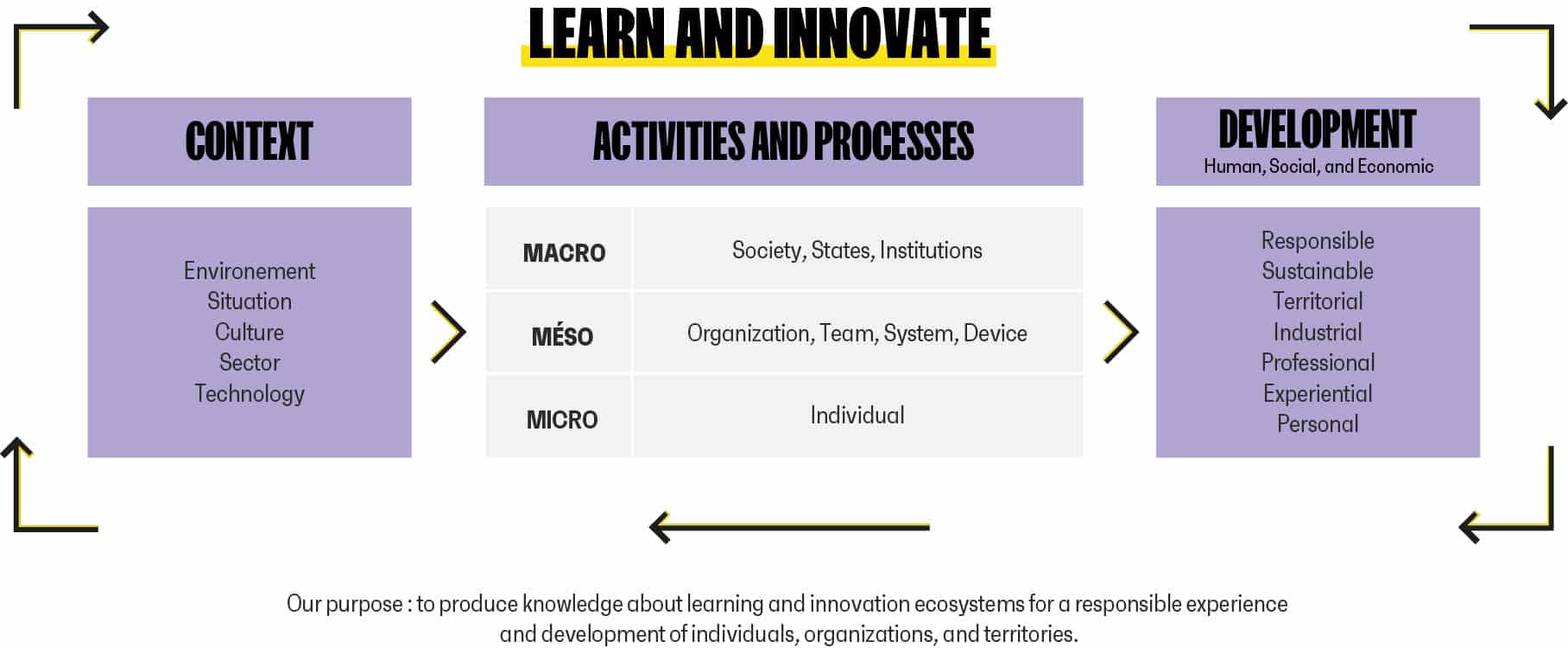
The figure below presents the structure of our scientific approach. It highlights the interactionist paradigm in which all our work is embedded: performance in terms of human, social and economic development is seen as the result of the interaction between situational factors (learning and innovation context, made up of elements of the social, technological, industrial, economic and cultural environment) and dispositional factors determining the Learning and Innovating Activities and Processes.
One of the specificities of our team is the richness and diversity of the levels of analysis of these interactions. Indeed, these interactions can be considered at the Micro level of the individual (e.g. when we are interested in the learner, the professional, or the end-user), at the Meso level of the team, the system or the organization (e.g. when we study a training system, a project-team or a company) and finally at the Macro level of the society (e.g. when we analyze the institutional policies, the regional, national or international measures).
Because of the diversity of the levels of analysis of learning and innovation activities and processes, our research, depending on the case, may target personal, professional, experiential development for the individual (learner, innovator, end-user…); social development within a learning collective, an organization or a community; economic development at the industrial or territorial level, etc. On the other hand, we adopt a common ethical framework of responsible and/or sustainable development for all our research.
Team composition
- BALAIAN Anna
- BARKAR Alisa
- BATAL Thibaut
- BLUTEAU Marie
- BONDESAN Pierre
- GAUDENS Lisa
- GUEZ Sarah
- JOLY Lola
- JOUANJUS Marion
- LANNUZEL Tristan
- LI Wanji
- MARTIN COESEL Anna
- SAVARIT Gaëtan